The Rise of Antibiotic Resistance: A Global Health Crisis
test Caption Scipol dll.
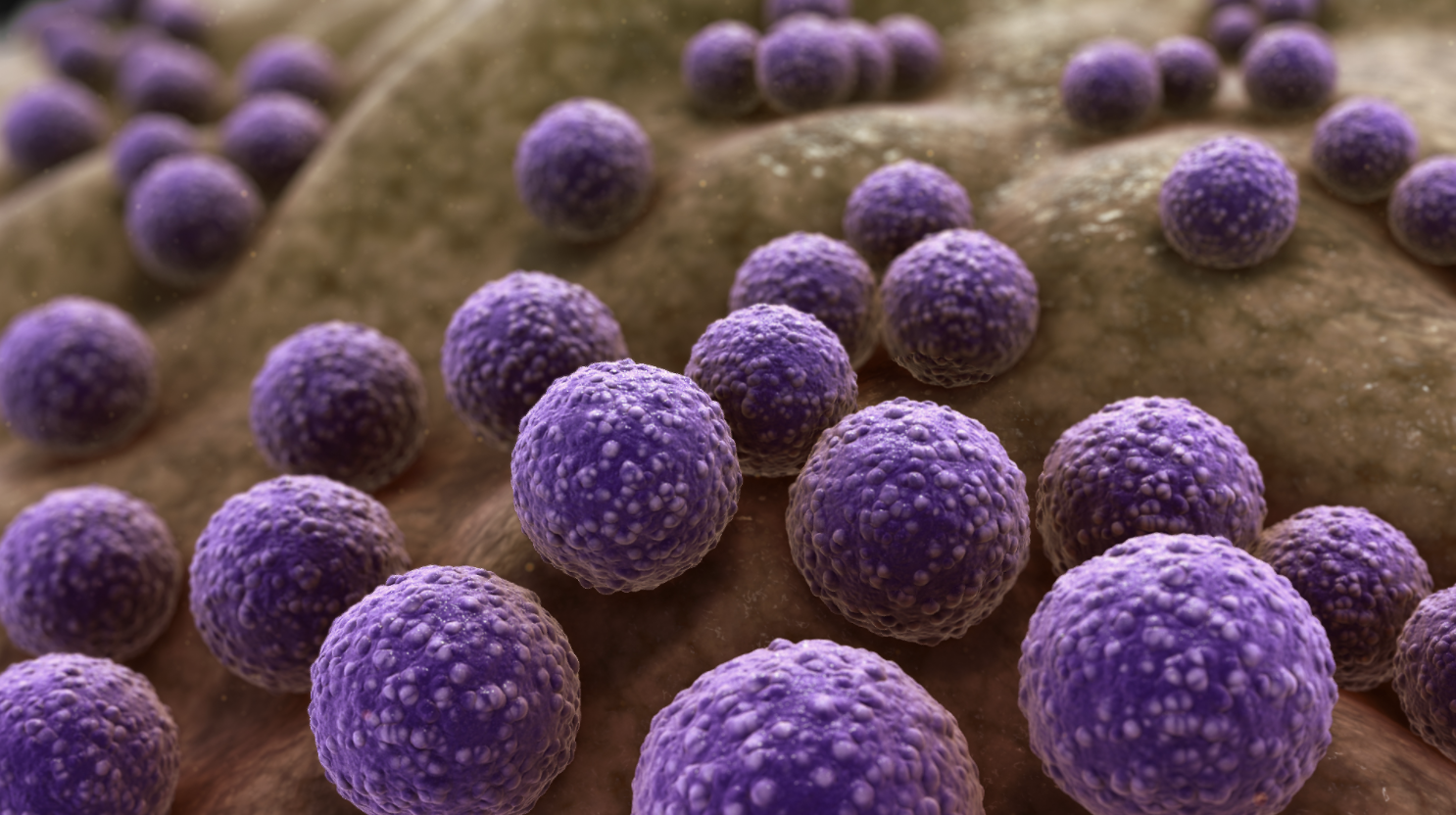
Antibiotic resistance is one of the most pressing health challenges of our time. With the increasing ineffectiveness of antibiotics, we are facing a potential global health crisis. Originally hailed as miracle drugs, antibiotics have saved millions of lives by treating bacterial infections. However, their overuse and misuse in medicine, agriculture, and livestock have accelerated the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, creating a major threat to public health worldwide. This article explores the causes, implications, and possible solutions to this growing problem, emphasizing why it demands immediate attention from individuals, healthcare systems, and governments alike.
1. Understanding Antibiotic Resistance: How It Occurs
Antibiotics work by killing bacteria or inhibiting their growth. However, bacteria are highly adaptive organisms and can develop resistance through natural selection. When exposed to antibiotics, some bacteria survive due to genetic mutations that provide them with resistance. These bacteria then reproduce, passing on their resistant traits, and eventually leading to a population of “superbugs” that standard antibiotics cannot kill.
Misuse and Overuse of Antibiotics
One of the leading causes of antibiotic resistance is the overuse and misuse of antibiotics. In many cases, antibiotics are prescribed unnecessarily—for example, to treat viral infections like the common cold, where they are ineffective. Over-prescription in human medicine, combined with the widespread use of antibiotics in agriculture and livestock, has led to high exposure levels for bacteria, accelerating resista
The Role of Self-Medication
Self-medication with antibiotics is a prevalent issue in some parts of the world, where individuals can purchase these drugs without a prescription. This practice often results in the incorrect use of antibiotics, such as taking them in inappropriate doses or for shorter durations, which gives bacteria more opportunities to develop resistance.
2. The Public Health Implications of Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance has far-reaching implications for global health. As bacteria become resistant to multiple drugs, infections that were once easily treatable can now lead to serious illness, prolonged hospital stays, and even death.
Rising Mortality and Morbidity Rates
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), antibiotic resistance already causes an estimated 700,000 deaths globally each year. Without effective antibiotics, common infections, minor injuries, and routine surgeries could become life-threatening. This alarming trend threatens to reverse decades of medical progress and could push us into a “post-antibiotic era.”
Increased Healthcare Costs
Antibiotic resistance also imposes significant economic burdens on healthcare systems. Treating resistant infections often requires more expensive drugs, prolonged hospital stays, and additional tests, placing a financial strain on both patients and healthcare providers. In some cases, the available antibiotics are not only more costly but also less effective and more toxic, further complicating patient care.
3. The Impact on Modern Medicine
Antibiotic resistance has the potential to undermine much of modern medicine. Procedures such as organ transplants, cancer treatments, and major surgeries rely on effective antibiotics to prevent and treat infections. Without these drugs, patients undergoing these treatments face increased risks, as they are more vulnerable to infections due to weakened immune systems.
Cancer Treatment and Immune-Compromised Patients
For patients undergoing chemotherapy, antibiotics play a crucial role in preventing infections. Antibiotic resistance makes it more difficult to manage infections in these vulnerable patients, putting them at higher risk. The same applies to people with chronic conditions like diabetes, who often require antibiotics for various infections throughout their lives.
Maternal and Child Health Risks
Pregnant women and newborns are also at risk in a world with limited antibiotic options. Antibiotics are essential for preventing infections during childbirth and managing postnatal infections in newborns. If resistant infections continue to rise, maternal and child mortality rates could increase significantly.





Comments (1)
admin
March 30, 2025asd;as